TITAN CMMS for Asset-Intensive Organisations
TITAN CMMS helps maintenance teams schedule preventive maintenance activities to keep assets and equipment increase its life span and efficiency. Maintenance scheduling can be complex in asset-intensive organisations, CMMS- preventive maintenance software schedules, organise and execute maintenance activities on time.

What is
Preventive Maintenance?
Preventive maintenance (or preventative maintenance) keeps your assets/equipment running with regular and routine maintenance activities. Preventive maintenance helps reduce the probability of equipment failure and unplanned machine downtime by scheduling maintenance based on real-time data insights. Different types of preventive maintenance include time-based, usage-based, predictive and prescriptive maintenance.


Kick-Start Your Preventive Maintenance & Reduced Downtime
Kick-Start Your Preventive Maintenance routine with Industry-Leading TITAN CMMS. Preventive maintenance primarily does 4 key actions;
Inspection: Regular inspection increase the reliability of assets and ensures a safe working environment.
Detection: Identify and fix issues at an early stage and reduce maintenance costs.
Correction: Address problems before it worsens by taking a proactive approach toward asset/equipment care.
Prevention: Do root cause analysis identify and prevent re-occurrence of equipment failures and increase productivity.
What are the Benefits of
Preventive Maintenance Software?
A preventive maintenance schedule will prevent equipment failure before it occurs and thereby save time, reduce costs, and increase productivity and efficiency.
- Increased life span of equipment/assets
- Less unplanned downtime due to equipment failure
- Fewer errors in day-to-day operations
- No unnecessary maintenance and inspections
- Improves reliability of equipment
- Equipment failures are fixed quickly
- Reduces risk of injury

TITAN CMMS - The Key to Optimise Maintenance Operations Smart Solution
Worried about managing maintenance operations? TITAN CMMS is here to help! TITAN help organisations track and manage all maintenance-related tasks, boosts asset efficiency and performance, by creating a maintenance request, breakdown request, just do it (JDI), and tasks, at any time from anywhere.
Start Free Trial Watch Video Tell a Friend
Refine your Preventive Maintenance Plans using a CMMS Software
Simplify the complex process of managing preventive maintenance tasks using a computerised maintenance management system. CMMS keep track of all maintenance-related inspections, replacements and repairs. Data stored in a single platform helps in effectively managing work orders, maintenance records and inventory and ensure maintenance operations are done smoothly.
Safeguarding Assets against Equipment Failures
Stay ahead of unexpected breakdowns by conducting regular maintenance and minimising costly equipment failures. Prolong the lifespan and reliability of your assets by minimising downtime and maximising productivity with a comprehensive preventative maintenance approach. Safeguard your assets and bottom line with effective preventative maintenance strategies. Maintain your equipment in good condition with a customised maintenance solution. Identify and mitigate any risks associated with asset downtime and ensure smooth and efficient operations.
Read More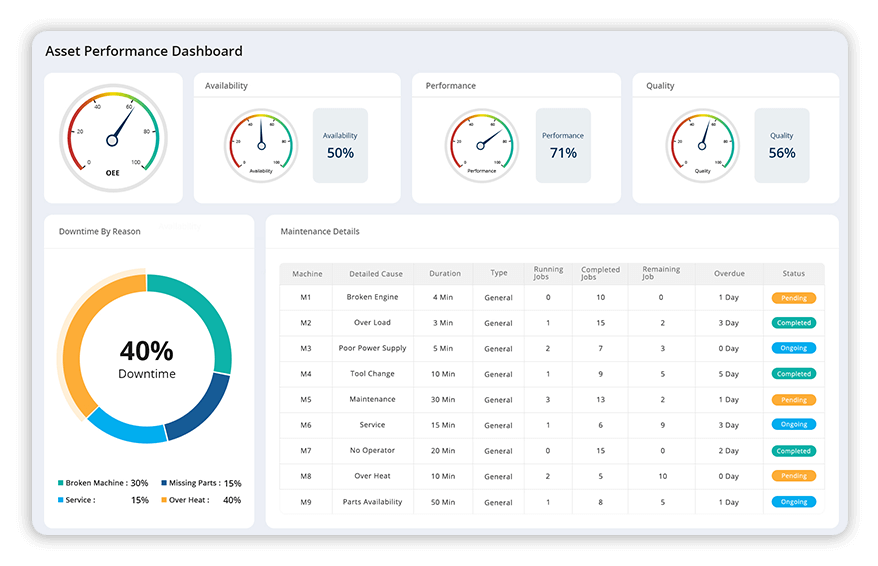

Streamlining Routine Maintenance Operations
Automate the planning, tracking, and scheduling of daily, weekly and monthly preventive maintenance tasks with CMMS software. Implement a maintenance schedule based on predefined intervals, metre readings, or runtime triggers. Say goodbye to manual scheduling and let the CMMS do it. Set up automated reminders, assign tasks to technicians hassle-free, and ensure timely completion of preventive maintenance activities, reducing the risk of equipment failure. Create detailed checklists for each preventive maintenance task, outlining the steps and materials required. These checklists serve as a guide for technicians, ensuring consistency and accuracy in their work.
Read MoreSimplify Work Order Management
Automatically generate work orders with the CMMS software when preventive maintenance tasks need to be performed and track and monitor the statuses in real time. Avoid tedious manual work order creation, saving time and ensuring maintenance tasks are never overlooked or delayed. Specify the equipment, set the maintenance schedule, assign technicians, and add any necessary instructions, all within a few clicks on your preventive maintenance journey. Automatically notify technicians when a maintenance task is due and allow them to confirm their attendance and add additional notes to the work order.
Read More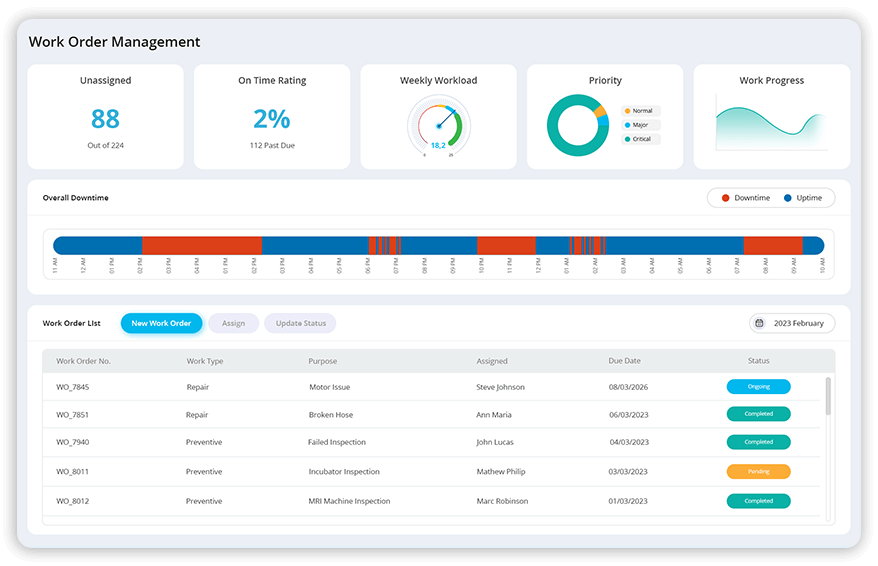

Real-time Notifications for Preventive Maintenance
Stay on top of preventive maintenance activities with customisable notifications and alerts in the CMMS software. Receive automated reminders of upcoming maintenance tasks, overdue work orders, or any critical maintenance issues that require immediate attention, and never miss a maintenance deadline again. Set up multiple notification levels for stakeholders so everyone is always in the loop. Ensure tasks are completed on time and critical issues are addressed quickly. Automated notifications can be tailored to user preferences, such as SMS messages, emails, or push notifications.
Preventive Maintenance Metrics Analysis
Track and measure the key metrics related to maintenance processes such as MTTR (Mean Time To Repair), MTBF (Mean Time Between Failure), and OEE (Overall Equipment Efficiency) to determine the effectiveness of maintenance practices. Optimise the maintenance activities, identify problem areas and improve the overall reliability and efficiency of the maintenance processes. Standardised maintenance practices can reduce failure rates and improve equipment efficiency. Increase the visibility of maintenance activities and operations by tracking and analysing these key metrics. This will help identify any inefficient processes and take corrective actions. Regular maintenance leads to improved performance and productivity. Tracking these metrics can help identify areas for improvement and cost savings.
Read More

Maintenance Logs and Automated Reports
Maintain a comprehensive preventive maintenance history for each asset in your inventory. Easily access information such as previous maintenance records, repairs, work orders and replacements. Attach details such as equipment specifications, warranties, and logs for reference. Track your assets' lifespan, identify recurring issues, and plan maintenance accordingly. Monitor and adjust maintenance plans in real-time and generate reports for future maintenance needs.
Read MoreEasy Integration with Existing Systems
Integrate CMMS with other systems, such as Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA), Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, or Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software and MES (Manufacturing Execution System), to provide adequate data exchange and improve preventive maintenance efficiency. Streamline preventive maintenance workflow and automate essential processes by utilising CMMS software. Analysing SCADA data to detect patterns and anomalies supports preventative maintenance. IoT sensors can provide real-time data to the CMMS regarding equipment status and condition. Integrating CMMS with ERP software and MES systems allows for streamlining processes and improving efficiency. Facilitate smooth and efficient data exchange for preventive maintenance tasks and ensure preventative maintenance processes are reliable and cost-effective.
Read More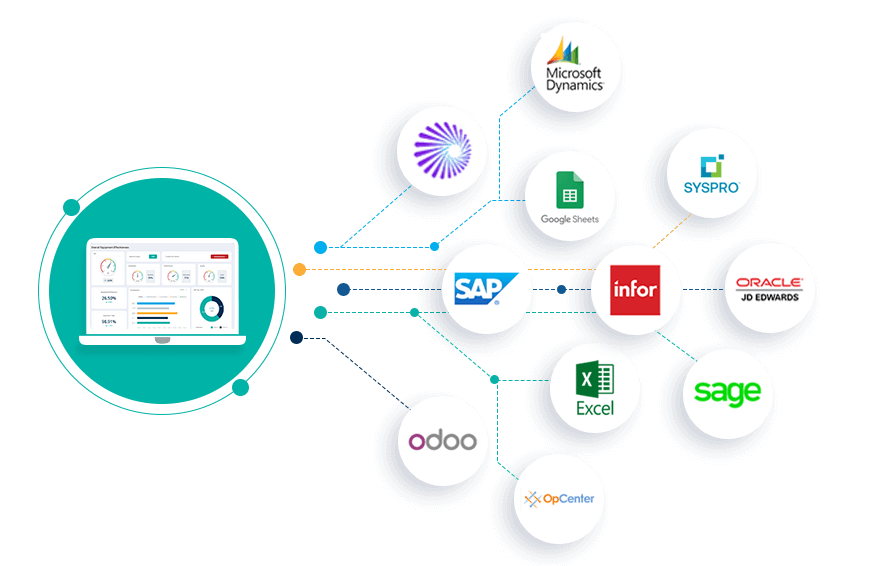

Enhanced Workplace Safety and Compliance
Schedule and track safety-related preventive maintenance tasks, such as equipment inspections and safety checks. Monitor safety conditions, track safety records, and provide alerts when violations are identified. Provide a secure environment for your team by ensuring compliance with safety regulations. Create detailed records of all maintenance activities to track potential safety hazards. Monitor the effectiveness of the preventive maintenance activities and make necessary adjustments with all-inclusive CMMS software.
Read MoreIncreased Efficiency and Reduced Energy Consumption
Reduce energy consumption during operational procedures in your workplace and find out where energy is wasted due to wear and tear of ageing equipment. Replace worn-out spare parts and assets which lack performance promptly. Identify changes in equipment usage patterns, trends and vibrations which lead to increased energy consumption and conduct regular maintenance and servicing of machines and equipment. Monitor any changes in equipment efficiency and replace obsolete equipment with more energy-efficient models.
Read More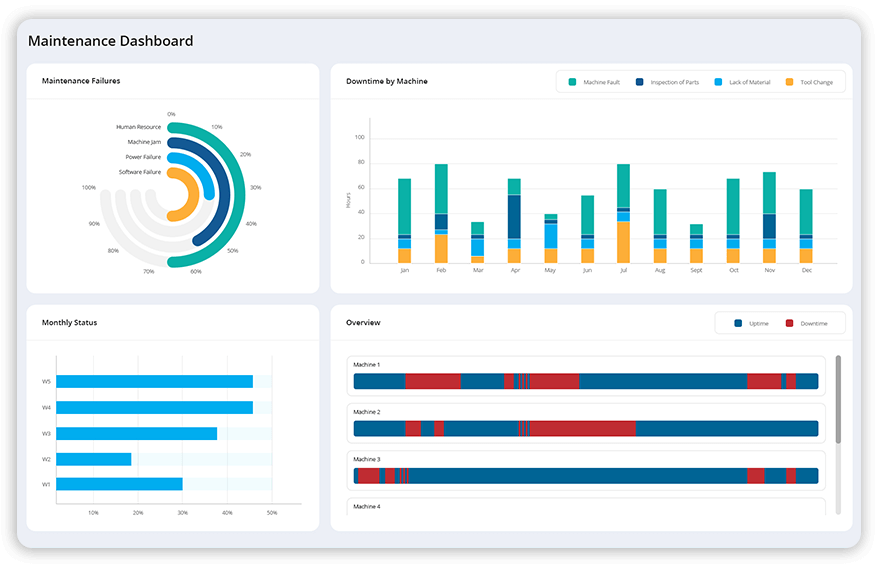
Contents
- What are the essential features to consider in a CMMS for effective preventive maintenance?
- How can CMMS help in creating and managing preventive maintenance schedules?
- How to set up a preventive maintenance program using CMMS?
- What role does preventive maintenance play in reducing equipment downtime and increasing productivity?
- How can a CMMS assist in prioritising preventive maintenance tasks based on criticality?
- What are the benefits of predictive maintenance?
- What are the six pillars of the predictive maintenance program?
What are the essential features to consider in a CMMS for effective preventive maintenance?
When choosing a CMMS (Computerised Maintenance Management System) for effective preventive maintenance, these essential features are worth considering.
- Preventive Maintenance Scheduling: The CMMS should have robust scheduling capabilities to create and manage preventive maintenance tasks based on time, metre readings, or usage triggers.
- Task Templates: Creating task templates allows for consistent and efficient generation of preventive maintenance work orders, ensuring all necessary steps and instructions are included.
- Work Order Management: The CMMS should have a comprehensive work order management module to track and prioritise preventive maintenance tasks, assign them to technicians, and monitor their progress.
- Equipment and Asset Management: A CMMS should provide a centralised database to store and manage equipment and asset information, including specifications, maintenance history, and documentation.
- Inventory Management: An integrated inventory management module helps track spare parts and supplies needed for preventive maintenance, ensuring adequate stock levels and minimising downtime.
- Mobile Access: Mobile compatibility allows technicians to access and update preventive maintenance tasks on the go, improving efficiency and enabling real-time data collection.
- Reporting and Analytics: The CMMS should offer reporting and analytics features to monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), track maintenance metrics, and identify areas for improvement.
- Alerts and Notifications: The system should be able to send automated alerts and notifications to maintenance teams and stakeholders regarding upcoming preventive maintenance tasks or any deviations.
- Integration Capabilities: A CMMS that can integrate with other systems like SCADA, IoT sensors, or ERP software enables seamless data exchange and enhances the effectiveness of preventive maintenance.
- Documentation and Attachments: The ability to attach relevant documents, manuals, images, or videos to preventive maintenance tasks enhances the clarity and effectiveness of instructions.
- Compliance and Regulations: The CMMS should support regulatory compliance by allowing the documentation of inspections, certifications, permits, and adherence to industry standards.
- User-Friendly Interface: A user-friendly and intuitive interface simplifies navigation and encourages user adoption across the maintenance team.
- Scalability and Customisation: The CMMS should accommodate the growth and changing needs of the organisation, allowing the customisation of fields, workflows, and reports.
- Training and Support: Adequate training resources and ongoing technical support from the CMMS provider ensure smooth implementation and troubleshooting when needed.
- Data Security: The CMMS should have robust security measures to protect sensitive maintenance data, ensuring confidentiality and preventing unauthorised access.
How can CMMS help in creating and managing preventive maintenance schedules?
- Centralised Scheduling: CMMS is a centralised hub where you can create and manage preventive maintenance schedules for all equipment and assets. It allows you to input maintenance tasks, set their frequencies, and enforce them to specific assets or equipment.
- Automated Task Generation: Once preventive maintenance tasks and schedules are defined in the CMMS, it can automatically generate tasks based on predetermined intervals, metre readings, or usage triggers. This automation saves time and ensures that scheduled maintenance activities are not overlooked.
- Recurring Task Management: The CMMS enables the creation of recurring preventive maintenance tasks, such as monthly inspections or quarterly calibrations. It automatically generates these tasks at specified intervals, eliminating the need for manual scheduling.
- Calendar Views: A CMMS typically provides calendar views, allowing maintenance managers and technicians to visualise the preventive maintenance schedule over time. This visual representation helps understand the workload distribution and identify overlapping or conflicting tasks.
- Prioritisation and Criticality: The CMMS can prioritise preventive maintenance tasks based on criticality or predefined criteria. This ensures that high-priority tasks receive attention and are scheduled accordingly.
- Resource Allocation: With a CMMS, you can assign the necessary resources, such as technicians, tools, and spare parts, to each preventive maintenance task. This feature helps optimise resource allocation and prevents conflicts or overbooking.
- Rescheduling and Reshuffling: If there are changes in the maintenance schedule due to unforeseen circumstances or operational requirements, a CMMS allows for easy rescheduling and reshuffling of preventive maintenance tasks. It updates the schedule and notifies relevant stakeholders of any changes.
- Real-Time Updates: CMMS systems often provide real-time updates and notifications to maintenance teams regarding scheduled preventive maintenance tasks. This ensures that technicians know their upcoming assignments and can plan their work accordingly.
- Compliance and Regulations: A CMMS can help manage compliance with regulatory requirements by incorporating them into the preventive maintenance schedule. It ensures that inspections, certifications, or other compliance-related activities are scheduled and performed as needed.
- Data Analysis: By capturing maintenance history in the CMMS, it becomes a valuable resource for analysing the effectiveness of preventive maintenance schedules. Maintenance managers can review historical data, identify patterns or trends, and make informed decisions to optimise future schedules.
How to set up a preventive maintenance program using CMMS?

The following enables streamlining scheduling, execution, and tracking maintenance tasks for improved asset reliability and operational efficiency.
- Define Maintenance Objectives: Clarify the goals and objectives of your preventive maintenance program. Determine the desired outcomes, such as increasing equipment reliability, reducing downtime, or extending asset lifespan.
- Identify Assets and Equipment: Create a comprehensive inventory of all assets and equipment that require preventive maintenance. Gather information such as equipment specifications, operating parameters, and maintenance history.
- Determine Maintenance Tasks: Identify the specific maintenance tasks that need to be performed on each asset or equipment. This may involve referencing manufacturer recommendations, industry best practices, or regulatory requirements. Categorise the tasks based on frequency (time-based or condition-based), complexity, and criticality.
- Establish Maintenance Frequencies: Determine the frequency at which preventive maintenance tasks should be performed for each asset. This can be based on time intervals (e.g. monthly, quarterly) or triggered by specific conditions (e.g. metre readings, sensor data).
- Set Maintenance Triggers and Thresholds: If using condition-based maintenance, define the triggers or thresholds that indicate when a maintenance task should be performed. This could be based on parameters such as temperature, vibration, fluid levels, or other measurable variables.
- Create Task Templates: Develop standardised task templates for each type of preventive maintenance task. Include step-by-step instructions, required tools or materials, safety precautions, and relevant documentation or references. These templates will serve as the basis for generating work orders in the CMMS.
- Enter Asset and Maintenance Data: Input asset information, including specifications, maintenance history, and any associated documentation, into the CMMS. This involves populating the system with accurate and up-to-date data for each asset.
- Schedule Preventive Maintenance Tasks: Utilise the CMMS to schedule preventive maintenance tasks based on the defined frequencies, triggers, and task templates. Assign tasks to specific assets, resources (technicians), and time slots on the calendar.
- Generate Work Orders: Use the CMMS to generate work orders for each scheduled preventive maintenance task automatically. These work orders should include all relevant information from the task templates, such as instructions, checklists, and required parts or tools.
- Assign and Dispatch Work Orders: Assign the generated work orders to the appropriate technicians or maintenance teams. Dispatch the work orders through the CMMS, ensuring technicians receive notifications and access to the necessary information.
- Execute Maintenance Tasks: Technicians perform the scheduled preventive maintenance tasks according to the instructions provided in the work orders. They record any observations, findings, or measurements during the maintenance process.
- Update CMMS with Maintenance Data: Technicians enter maintenance data into the CMMS, including completion dates, hours spent, materials used, and any issues encountered. This data is essential for tracking maintenance history and analysing performance.
- Monitor and Analyse Performance: Utilise the reporting and analytics features of the CMMS to monitor the performance of the preventive maintenance program. Assess key performance indicators (KPIs), such as asset uptime, maintenance costs, and schedule adherence. Identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to optimise the program.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update the preventive maintenance program based on feedback, data analysis, and evolving equipment needs. Adapt the program as necessary to ensure its effectiveness in achieving maintenance objectives.
What role does preventive maintenance play in reducing equipment downtime and increasing productivity?
Preventive maintenance is crucial in reducing equipment downtime and increasing productivity by addressing potential issues before they lead to failures or breakdowns.
- Early Detection of Problems: Regularly scheduled preventive maintenance allows technicians to inspect and assess equipment for any signs of wear, degradation, or potential issues. By identifying and addressing problems early on before they escalate into major failures, preventive maintenance helps prevent unexpected breakdowns and minimises equipment downtime.
- Equipment Reliability and Performance: By performing regular maintenance tasks, such as lubrication, calibration, and cleaning, preventive maintenance ensures that equipment operates at its optimal performance levels. This enhances reliability and reduces the likelihood of unexpected failures or malfunctions that disrupt operations and productivity.
- Prolonged Equipment Lifespan: Preventive maintenance helps extend the lifespan of equipment by ensuring it is well-maintained and operates within designed specifications. Regular inspections, component replacements, and adjustments help prevent premature wear and deterioration, allowing equipment to function effectively for longer.
- Minimised Reactive Maintenance: Reactive maintenance, which involves fixing equipment after it fails, is often more time-consuming, costly, and disruptive to operations. By proactively addressing maintenance needs through preventive maintenance, organisations can reduce the frequency and severity of reactive maintenance, leading to less downtime and improved productivity.
- Planned Maintenance Activities: With a preventive maintenance program, maintenance activities can be scheduled during planned downtime or non-production periods. This minimises the impact on regular operations and ensures that maintenance tasks are completed efficiently without causing significant disruptions or delays.
- Improved Equipment Efficiency: Preventive maintenance optimises equipment efficiency by addressing factors that may lead to decreased performance or energy wastage. Tasks such as cleaning or replacing filters, adjusting settings, and calibrating equipment contribute to improved efficiency, reducing energy consumption and increasing productivity.
- Enhanced Safety: Preventive maintenance involves safety inspections and checks, ensuring that equipment meets safety standards and regulations. By identifying and addressing potential safety hazards or risks, preventive maintenance contributes to a safer working environment, reducing the likelihood of accidents or injuries that can result in operational disruptions.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: A well-implemented preventive maintenance program generates valuable data on equipment performance, maintenance history, and trends. This data can be analysed to identify patterns, make informed decisions about equipment upgrades or replacements, and optimise maintenance strategies, further reducing downtime and enhancing productivity.
How does CMMS assist in prioritising preventive maintenance tasks based on criticality?
- Asset Criticality Classification: CMMS allows you to assign a criticality classification to each asset or equipment within the system. This classification can be based on factors such as the asset's impact on operations, production, safety, regulatory compliance, or financial implications.
- Risk Assessment and Scoring: The CMMS can incorporate risk assessment methodologies to evaluate the potential risks associated with each asset. By assigning risk scores based on factors like failure consequences, likelihood, and detectability, the CMMS helps determine the criticality level of assets.
- Priority Codes or Levels: Within the CMMS, you can assign priority codes or levels to preventive maintenance tasks. These codes indicate the relative importance or urgency of completing each task. The criticality classification and risk assessment can inform the assignment of appropriate priority codes to tasks.
- Maintenance and Failure History: The CMMS maintains a maintenance history log and tracks equipment failure incidents. By analysing this data, the system can identify assets with a history of frequent failures or significant impact on operations. Such assets can be given higher priority for preventive maintenance tasks.
- Equipment Condition Monitoring: CMMS can integrate with condition monitoring systems, IoT sensors, or other data collection methods to gather real-time data about equipment health. By continuously monitoring equipment conditions, the CMMS can identify assets that require immediate attention or have critical condition thresholds, prioritising preventive maintenance accordingly.
- Work Order Queues and Scheduling: The CMMS manages work order queues and scheduling based on priority codes assigned to preventive maintenance tasks. This ensures that higher-priority tasks are scheduled and executed before lower-priority ones, reducing the risk of critical failures and associated downtime.
- Real-time Notifications: In the event of critical asset conditions or impending failures, the CMMS can trigger automated alerts, notifications, or escalation workflows. These notifications can be sent to maintenance teams, supervisors, or stakeholders, ensuring timely attention and prioritisation of preventive maintenance tasks.
- Reporting and Analytics: The CMMS provides reporting and analytics capabilities to analyse maintenance data, including criticality ratings, asset performance, and maintenance history. These insights can help identify trends, prioritise preventive maintenance actions for critical assets, and make data-driven decisions to optimise maintenance strategies.
What are the benefits of Predictive Maintenance?
Streamline your facility management operations with predictive maintenance! Organisations risk performing too much maintenance and wasting resources or having to deal with mechanical failures if they rely solely on preventive maintenance strategies. Reactive maintenance, on the other hand, is performed only when needed causing a high cost of unscheduled downtime. Predictive maintenance operations address these concerns as the maintenance work is scheduled exclusively when the specific conditions are met and before the assets break down. Listing the benefits down can give you a better idea.
- Lesser equipment failures As equipment failures can bring serious outcomes, regular monitoring of the equipment and process system’s conditions stands inevitable. Condition monitoring maintenance techniques allow facility managers to get real-time data about asset health and take necessary actions beforehand.
- Reduced MTTR (Mean time to Repair) By lowering machine failures and breakdowns, predictive maintenance can also lessen the time required to repair or recondition plant equipment. As soon as the sensors indicate something is wrong with the equipment and it might break down soon, technicians have the advantage of fixing it then and there before the damage gets larger.
- Increased asset lifetime Detecting machine and system problems at the earliest can increase the service life of the facility machinery by an average of 30%. The implementation of the predictive maintenance strategy can reduce not only the severity of damage but also decrease the propagation of defects. Every issue, even in an inexpensive part, can damage any crucial part, reducing the asset lifecycle.
- Precise asset data Predictive maintenance uses sensor data to predict the Mean Time Between Failures (MTFB). Having access to this data can allow the facility manager to determine the most cost-effective time to replace the machinery rather than scheduling costly maintenance tasks that won’t maintain the equipment in optimal condition in the long run. CMMS software allows viewing the maintenance and continuing operations costs that exceed the replacement costs.
- Verification of the repair effectiveness Predictive maintenance sensors conduct various actions like vibration analysis, oil analysis, thermal imaging, equipment observation, etc., verifying whether the repair was successful before the machine starts again.The need for a second shutdown to adjust the inadequate or incomplete repairs is not a question anymore.
- Improved Workplace safety Do not worry about your risk management or workplace safety anymore! Accidents in the workplace, especially the ones related to machine failures, are not only dangerous but cause substantial financial impacts. Early detection of the problem can reduce the risk of catastrophic failures and avoid injuries.
- Increased Returns Maintenance teams invest fewer resources in maintenance tools and services by avoiding complex machine breakdowns. Maintenance technicians and managers can increase work productivity by having more time to focus on vital maintenance tasks. Also, optimising the equipment conditions can reduce machine downtime, directly affecting the bottom line.
What are the six pillars of the predictive maintenance program?
Technology is only one among the many factors that contribute to the predictive maintenance program. Let’s probe the six pillars that strongly impact a strong predictive maintenance program and how they can contribute to achieving the preferred outcomes.
- PEOPLE: The predictive maintenance journey starts with the people. Every other pillar of the predictive maintenance program needs the people to build and maintain them. Data needs interpretation. Technology needs to be set up and managed. This is why everyone in the organisation needs to understand how a PdM works and why it is essential.
- DATA: A lot of information is required for a predictive maintenance program. Without accurate data from the shop floor, your efforts in identifying or predicting anomalies are wasted, and your decisions go wrong. Only data can establish the essential link between the existing asset performance and the future state of the asset. That’s why everything about the assets needs to be constantly updated.
- PROCESS: The plans and the ideas the maintenance team put forth, and it is executed, form the processes. It can either be people-driven or equipment driven. People process can be how your maintenance team do their work, which outlines how the staff interact with the machines, data, and everything else. On the other hand, equipment processes are vital as they incorporate what operations your equipment completes, how to capture asset data and how the data maps to future performance.
- TOOLS & PARTS: Tools are the instruments needed to measure the asset’s conditions and those required to inspect and repair equipment. Parts are the different elements of the equipment. Both these play an inevitable role in the predictive maintenance strategy.
- EQUIPMENT: It is essential to know which of your equipment allows you to anticipate failure on it while setting up a predictive maintenance program. The assets that fit into the predictive maintenance programs are the ones that provide good condition data with enough lead time to catch the problems before the failure occurs. Apply your predictive maintenance strategies to the most critical assets with the most observable failure modes.
- TECHNOLOGY: Technology binds all the other ingredients together and helps you manage, facilitate and optimise the other pillars of predictive maintenance. To understand how to carry out the maintenance strategy, you need to have a lot of data from various sources. What products are being run, when, the cost of all activities, and when was the last maintenance done? All these data are captured, stored and analysed with the help of several technologies like ERP, MES or CMMS software systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Inspection: Regular inspection increases the reliability of assets and ensures a safe working environment.
- Detection: Identify and fix issues at an early stage and reduce maintenance costs.
- Correction: Address problems before it worsens by taking a proactive approach toward asset/equipment care.
- Prevention: Do root cause analysis identify and prevent re-occurrence of equipment failures and increase productivity.
- Establish priorities and goals.
- Create a task list and an asset inventory.
- Organise your resources and priorities.
- Set up KPIs for the planned preventative maintenance.
- Review and improve.


